Manufacturing has come a long way. Just a few years ago, the idea of manufacturing something in your home was unheard of. If you wanted something, you had to buy it. Or, you had to work with a company to get it produced for you.
Now you can buy a machine that you can set up in your house, and with your computer, you can produce just about anything you can dream of. Your only limitations are your imagination and the software on your computer.
What used to cost companies hundreds, if not thousands, of dollars to do, can now be done for a fraction of the price in your living room.
So what changed? What’s allowing us to create in our living rooms now that wasn’t around before? This article will explore those questions and more.
What Is Additive Manufacturing?
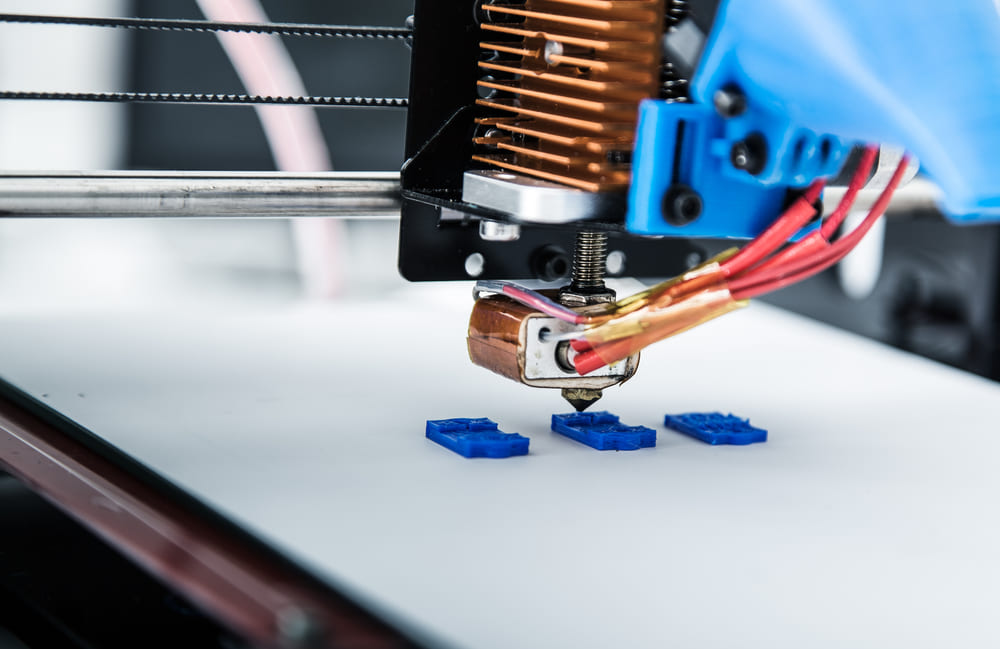
In the old days, if we wanted to make something, we had to start with our material, and then take away everything we didn’t need. We’ve all heard the famous Michelangelo quote, “I saw the angel in the marble and carved until I set him free.”
That’s the basis of subtractive manufacturing. Michelangelo started with a chunk of marble, envisioned what he wanted out of it, and then carved away the excess marble until he had his finished product.
Additive manufacturing is the exact opposite of that. You start with nothing and then add in what you need.
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, creates by using technologies that add layer-upon-layer of material until your product is done. The material can be anything from plastic, metal, concrete and, one day, maybe even human tissue.
To 3D print, you need a computer, 3D print software, also known as computer-aided design or CAD software, a 3D printing machine, and the materials you choose to use for your project.
Once you’ve sketched your design using your CAD software, your machine reads the sketch and then lays down layer upon layer of your material until it’s turned your sketch into a 3D object.
While 3D printing is the most common form of additive manufacturing, it also encompasses technologies like rapid prototyping, direct digital manufacturing, layered manufacturing, and additive fabricating.
The potential uses of additive manufacturing are endless. It started as a way to make prototypes for companies. They could think of a product, make a sketch, and have a sample in their hands in record time.
It could end up revolutionizing industries like healthcare, being able to create actual human tissue.
Think about that for a second.
We might be able to produce human tissue. Think of the lives that are going to change. Think about how much that will improve the quality of life for millions upon millions of people.
This will be much more than prototyping. This is life-changing technology.
Additive Manufacturing Processes

There are several different processes used in additive manufacturing.
Material Extrusion
Material extrusion is the most well-known process. This is how most 3D printers will function. With material extrusion, your material comes in a spool, which is pulled through a heated nozzle mounted on a movable arm. The nozzle moves horizontally while the nozzle moves vertically, depositing your melted material layer by layer. Precise temperatures in your machine allow for proper adhesion.
Direct Energy Deposition
DIrect energy deposition is very similar to material extrusion, but it allows for more materials to be used. Plastics are common with material extrusion. With direct energy deposition, you can use polymers, ceramics, and metals. A laser or electron beam gun is used to melt your material layer by layer.
Material Jetting
Material jetting uses a print head much like an inkjet printer. The head moves on x, y, and z-axes to create the 3D object. The layers will harden as they cool, or they can be cured by ultraviolet light.
Binder Jetting
Binder jetting is extremely similar to material jetting, except with binder jetting the print head lays down a powder that uses a liquid adhesive.
The Advantages Of Additive Manufacturing
First of all, additive manufacturing allows people and companies to create lighter, more complex designs that have been too difficult to produce using traditional methods.
Additive manufacturing is excellent for rapid prototyping. Since the entire process is digital, it eliminates the need for several steps that you would have to take using traditional methods. It lets companies make prototypes on the run, instead of waiting days or weeks for the prototypes.
No matter what your reason for using additive manufacturing, your lead times, in general, are significantly reduced. For example, lead times for certain jet engine parts have been reduced by an entire year. That is huge for the aerospace industry.
Designs that would traditionally require several different parts, and several different intermediaries, can now be created in one shot with additive manufacturing. The lead times, as well as cost savings here, are apparent.
It’s always been a goal for engineers to reduce the weight of an object while improving the strength. With additive manufacturing, this is possible. There have been cases where an additive manufactured product weighed 84% less than it’s the original counterpart while being just as strong.
Added Complexity
Additive manufacturing is allowing engineers to build more complex structures than they ever have before. Objects that used to require assembly or welding of multiple pieces can now be made in one shot with the additive manufacturing process. The capabilities of traditional machinery no longer restrict designers and engineers.
Saving Time
The entire process saves a lot of time. You can go straight from the CAD file to your machine without the need for any middlemen or special machinery. You can even make changes during the process without having to wait while you send off for the changes and wait for them to be approved.
Saving Materials
With additive manufacturing, you are no longer starting with a large piece of your material and then getting rid of what you don’t need. That creates a lot of wasted material. With additive manufacturing, you start with your material and add it layer by layer until your design is complete — no wasted material.
The Worlds Largest Additive Manufacturing Company

GE, the worlds largest manufacturing, could soon be the worlds largest additive manufacturing company. Their aviation division is preparing to produce a fuel nozzle for an aircraft engine using additive manufacturing, rather than casting and welding the material like they previously have done.
This has the potential to change how GE designs and manufactures everything from the parts in an ultrasound machine to gas turbines.
The company is already using the process in certain niche industries like medical implants, but using it to produce a metal alloy part that will be used in thousands of jet engines is genuinely revolutionary.
3D printing for personal and small business use has gained a lot of publicity recently, but it the technology will have the most significant impact when the multinational corporations adopt it like GE.
GE chose to use the additive process for its fuel nozzles for the obvious reasons listed above. It uses less material, saving the company both time and money.
Because the material GE is using will be lighter than the materials used for the original fuel nozzle, it will also produce significant fuel savings for the airlines.
Not only will it be lighter, but instead of being made up of over 20 parts using the traditional methods, it will be one uniform part using the additive manufacturing techniques.
It’s Flipping Entire Industries Upside Down

Additive manufacturing is obviously more than just 3D printing toys at your house. It’s revolutionizing the way things are designed and made, saving resources, time, and money. It’s already making an impact on several industries.
Education
3D printers can be a potent learning tool in classrooms. Students studying subjects like physics, chemistry, and engineering will be able to develop real-world skills using the printers.
Geography students could learn a lot more using a 3D printed topography map. Biology students can print cross-sections of different body parts and organs.
Engineering and graphic design students are the most obvious beneficiaries of the technology because they can turn their ideas into a reality in record time.
Healthcare
This is the most exciting industry that stands to benefit from additive manufacturing. We’re not able to print functioning organs yet, but the revolution in the healthcare industry is already underway.
3D printing will allow doctors to gain time and increase precision in their work, helping them better serve their patients.
In the dental field, dentists are already using 3D printing to make custom-made implants for their patients.
There is even a 3D printed drug that is being used to treat epilepsy.
Defense
The potential here is enormous, just on cost savings alone. The U.S. Navy already has plans to turn its ships into “floating factories” filled with 3D printers. The goal here is to be able to manufacture certain parts and supplies on board, so they are less dependent on potentially dangerous and unpredictable resupplies at sea.
We’re Witnesses To The Revolution
We have only reached the tip of the iceberg of what additive manufacturing can do. The idea of creating things at home using our computers and a 3D printer is fun, but this technology is destined to change the world.
Aerospace, health, automotive and education are just a few of the industries ripe for change. The environment will also benefit as we are producing less waste, and cut out technologies that pollute the atmosphere.
Before you know it, we’ll wonder how we survived before the rise of additive manufacturing.
Resources:
source: https://www.iqsdirectory.com/resources/everything-you-need-to-know-about-additive-manufacturing/